Vitamin E is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining good health. It is an antioxidant that helps protect the body from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules produced during metabolism. Vitamin E also supports the immune system, promotes healthy skin and eyes, and may even help prevent chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
In this article, we will explore the many health benefits of vitamin E and its nutritional sources. We will discuss how much vitamin E you need each day, how to get it through your diet or supplements, and what happens if you don’t get enough of this essential nutrient.
Overview of vitamin E and its importance
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble nutrient that plays a crucial role in the body’s immune system and cell function. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can lead to chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer. Vitamin E also helps to maintain healthy skin, eyesight, and neurological function.
There are eight forms of vitamin E, but alpha-tocopherol is the most active form in the human body. The recommended daily intake for vitamin E varies depending on age and gender but ranges from 15 mg/day for adults to 200 mg/day for pregnant women.
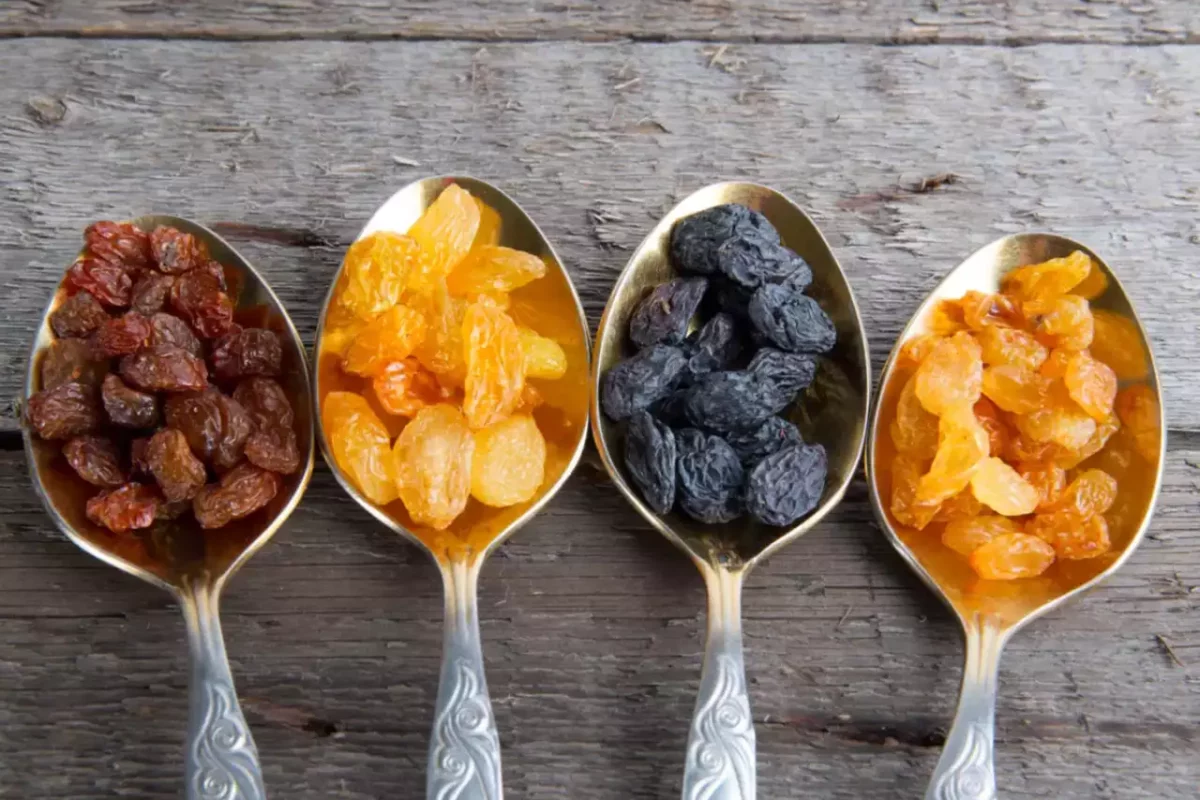
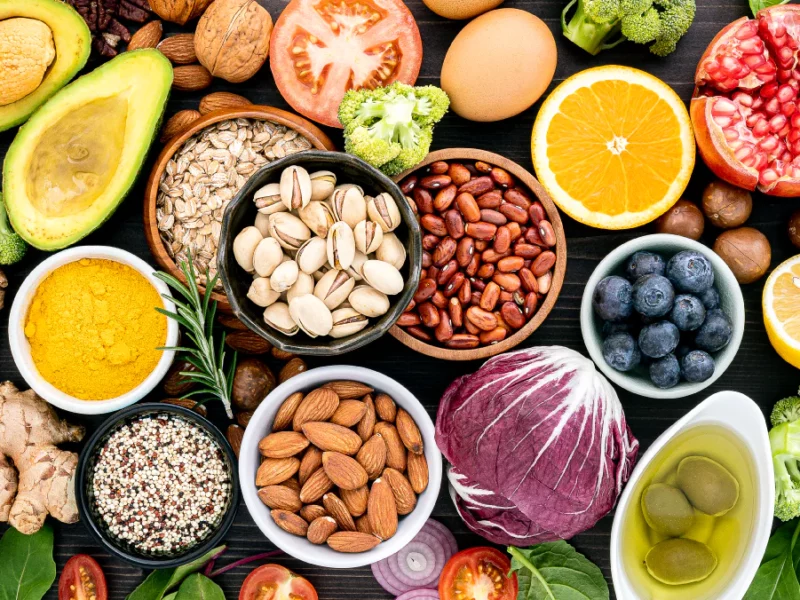
Good dietary sources of vitamin E include nuts (especially almonds), seeds (such as sunflower seeds), vegetable oils (such as wheat germ oil), leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals. However, it can be challenging to get enough vitamin E through diet alone, making supplementation an option for some people. Overall, getting enough vitamin E is essential for maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases.
Health benefits:
Vitamin E is known for its antioxidant properties that help protect cells from damage caused by environmental factors such as pollution, radiation, and smoking. It also plays an important role in maintaining healthy skin and eyes, boosting the immune system, and preventing chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease. Some studies have shown that taking vitamin E supplements may reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
One of the key functions of vitamin E is to boost immunity by stimulating the production of white blood cells which fight against infection and disease. It also helps regulate inflammation within the body which can contribute to chronic conditions such as arthritis. Additionally, vitamin E has been found to support cardiovascular health by reducing oxidative stress and improving blood flow.
While obtaining sufficient amounts of vitamin E through diet alone may be challenging for some individuals, there are a variety of food sources rich in this nutrient including nuts (particularly almonds), seeds (such as sunflower seeds), leafy green vegetables (spinach) and fortified cereals. For those who struggle to consume enough vitamin E through their diet alone, supplements are available in various forms including capsules, tablets, or liquid drops.
Antioxidants, immune system support, skin health
Antioxidants are essential for maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can lead to cancer and other illnesses. This vitamin also supports the immune system by enhancing the production of white blood cells, helping to fight off infections and diseases.
In addition to its antioxidant and immune-boosting properties, vitamin E is known for its ability to promote healthy skin. It helps maintain skin elasticity, reduces inflammation, and protects against sun damage. Vitamin E may also help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, making it a popular ingredient in many anti-aging products.
To get enough vitamin E in your diet, focus on incorporating foods such as nuts (especially almonds), seeds (such as sunflower seeds), avocadoes, spinach, broccoli, sweet potatoes, and oils (such as olive oil) into your meals. Alternatively, you can opt for vitamin E supplements after consulting with a doctor or nutritionist. Adequate intake of this nutrient will provide you with all these benefits that are crucial for living a healthy life.
Also Read: WELLHEALTHORGANIC.COM:ALCOHOL-CONSUMPTION-GOOD-FOR-HEART-HEALTH-NEW-STUDY-SAYS-NO
Nutritional sources:
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. This essential nutrient is also known for its ability to support healthy immune function, promote skin health, and improve cognitive function. While vitamin E can be obtained through supplements, it’s always best to get your daily dose of this nutrient from whole foods.
Some of the best nutritional sources of vitamin E include nuts and seeds like almonds, sunflower seeds, hazelnuts, and peanuts. These are great options for adding vitamin E to your diet as they’re easy to snack on or add to salads or smoothies. Other excellent sources include avocadoes, spinach, sweet potatoes, olive oil, and trout.
It’s worth noting that while vitamin E is essential for good health in small amounts; taking too much of this nutrient can lead to adverse effects like nausea and diarrhea. Therefore it’s important not to exceed the daily recommended intake of 15mg per day unless advised by a healthcare provider.
Nuts, seeds, leafy greens, vegetable oils
Nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and vegetable oils are all great sources of vitamin E. This fat-soluble nutrient is important for maintaining healthy skin and eyes, as well as supporting the immune system. Vitamin E also acts as an antioxidant in the body, helping to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Some of the best sources of vitamin E include almonds, sunflower seeds, spinach, and avocado oil. Other nuts like peanuts and hazelnuts are also high in vitamin E. Leafy greens like kale and broccoli is excellent sources of this nutrient too. Vegetable oils such as olive oil and wheat germ oil are rich in vitamin E as well.
It’s important to note that getting enough vitamin E through diet alone can be difficult for some people. Those with certain digestive disorders or who do not consume a balanced diet may benefit from taking a daily supplement containing this nutrient. However, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Recommended daily intake:
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin E varies depending on age, gender, and overall health. According to the National Institute of Health, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for adults is 15mg or 22.4 IU per day. Pregnant women also require a slightly higher dose at 15mg or 22.4 IU per day while breastfeeding mothers require even more at 19mg or 28.5 IU per day.
It’s important to note that too much vitamin E can be harmful, particularly in supplement form which can cause nausea, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal issues. The best way to ensure adequate intake is by consuming a variety of foods rich in Vitamin E such as almonds, sunflower seeds, spinach, and avocados.
Overall, it’s important to strive for a balanced diet that meets your individual nutritional needs rather than relying solely on supplements or specific vitamins and minerals. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your nutrient intake or supplementation.
Also Read: WELLHEALTHORGANIC.COM:WEIGHT-LOSS-IN-MONSOON-THESE-5-MONSOON-FRUITS-CAN-HELP-YOU-LOSE-WEIGHT
Adults’ and children’s recommended intake
When it comes to the recommended intake of vitamin E, adults, and children have different needs. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for adult males and females is 15 mg or 22.4 IU, while pregnant women require slightly more at 15.6 mg or 23.4 IU per day. For children aged one to three years old, the RDA is 6 mg or 9 IU per day, while for those aged four to eight years old, it increases to 7 mg or 10.4 IU.
It’s important to note that these recommendations are based on healthy individuals with no underlying medical conditions that may require higher doses of vitamin E. In some cases, individuals may need more vitamin E due to malabsorption issues or certain health conditions such as cystic fibrosis or liver disease.
To ensure adequate intake of vitamin E in both adults and children, a balanced diet rich in whole foods such as nuts and seeds, leafy greens, and vegetable oils can be beneficial. However, supplementation should only be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid potential adverse effects from high doses of vitamin E.
Risk factors associated with vitamin E deficiency include conditions that limit the absorption of fat, such as cystic fibrosis and liver disease. People with a low-fat diet or those who have undergone weight loss surgery may also be at risk of vitamin E deficiency. Premature infants and people with certain genetic disorders may require higher doses of vitamin E to prevent deficiencies.
On the other hand, excessive intake of vitamin E supplements can be harmful and increase the risk of bleeding in some individuals. People taking blood-thinning medications should consult their doctor before taking supplements containing vitamin E. Additionally, high doses of supplemental vitamin E may interact with medications used for chemotherapy, hypertension, and cholesterol management.
Overall, it is important to maintain a balanced diet that includes sources of natural vitamins like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds rather than relying solely on supplements to meet daily nutritional needs. Consultation with a healthcare provider can help identify any potential risks associated with supplementation or dietary changes for individuals at risk for deficiencies or excesses in certain nutrients like vitamin E.
Deficiency risks and overdose symptoms
Deficiency risks and overdose symptoms associated with Vitamin E intake are relatively rare. However, individuals who do not get enough Vitamin E in their diet may develop problems like muscle weakness, vision disorders, and anemia. In more severe cases, it can result in liver or neurological damage.
On the other hand, consuming excessive amounts of Vitamin E supplements can also lead to adverse health effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. Moreover, high doses of this vitamin can interfere with blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. Thus it is essential to stick to the recommended daily dosage for this nutrient which varies according to age and gender.
In conclusion, while a balanced diet rich in natural sources of Vitamin E is unlikely to cause any adverse effects on health; taking dietary supplements without proper guidance from a professional healthcare provider can be harmful. It’s necessary to remember that overconsumption or under-consumption of nutrients is equally undesirable for maintaining good health.
Also Read: WELLHEALTHORGANIC.COM:AMAZING-BEAUTY-TIPS-OF-ICE-CUBE-WILL-MAKE-YOU-BEAUTIFUL-AND-YOUNG
Conclusion:
In conclusion, vitamin E is a crucial nutrient that plays an essential role in maintaining optimal health. It acts as an antioxidant and protects the body’s cells from damage caused by free radicals. This helps to prevent chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. Vitamin E also supports healthy skin, hair, and nails by promoting cell growth and regeneration.
While it is possible to obtain adequate amounts of vitamin E through a balanced diet that includes foods such as nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and fortified cereals, some people may benefit from taking supplements. However, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Overall, incorporating vitamin E into your diet can have numerous health benefits and support overall wellness. By ensuring that you are consuming enough of this vital nutrient through food or supplements, you can help protect your body against oxidative stress and promote long-term health.